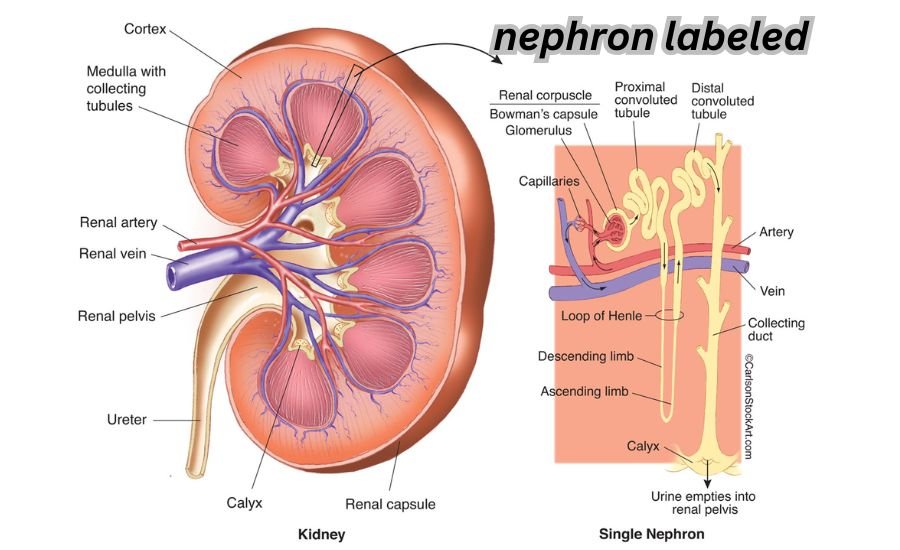
The nephron, a tiny yet vital structure in our kidneys, is responsible for filtering blood and maintaining the body’s balance of fluids and electrolytes. Understanding how a nephron is labeled can provide clarity about its function and its role in maintaining overall health. Welcome to blogrouters.com, where we simplify complex topics for everyone. In this article, we will dive deep into the anatomy of the nephron, explore its labeled parts, and explain their importance in a clear, easy-to-understand manner.
What is a nephron labeled, and Why is It Important?
The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering waste, excess water, and other impurities from the blood. Each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons, working tirelessly to maintain the body’s internal environment. To better understand this process, it’s essential to learn about the labeled parts of a nephron.
The Structure of the Nephron Labeled
A nephron consists of two main sections:
- The Renal Corpuscle: Includes the glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule, where filtration begins.
- The Renal Tubule: Includes the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, distal tubule, and collecting duct.
Each component has a specific function, ensuring the kidneys perform efficiently.
Why is Labeling Important?
Labeling the nephron’s parts helps students, healthcare professionals, and researchers understand its structure and function, allowing better insights into kidney health and related diseases.
Detailed Breakdown of Nephron Labeled Parts
Renal Corpuscle: The Starting Point
The renal corpuscle initiates the filtration process. It consists of two primary components:
- Glomerulus: A cluster of tiny blood vessels where filtration occurs.
- Bowman’s Capsule: Surrounds the glomerulus, collecting the filtered fluid.
This stage ensures that large molecules like proteins and cells remain in the bloodstream, while smaller molecules pass through.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
The proximal tubule is the first section of the renal tubule. It reabsorbs essential nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and ions, sending them back into the bloodstream.
Using labeled diagrams of the nephron, you can see how the PCT plays a crucial role in preventing nutrient loss while removing waste.
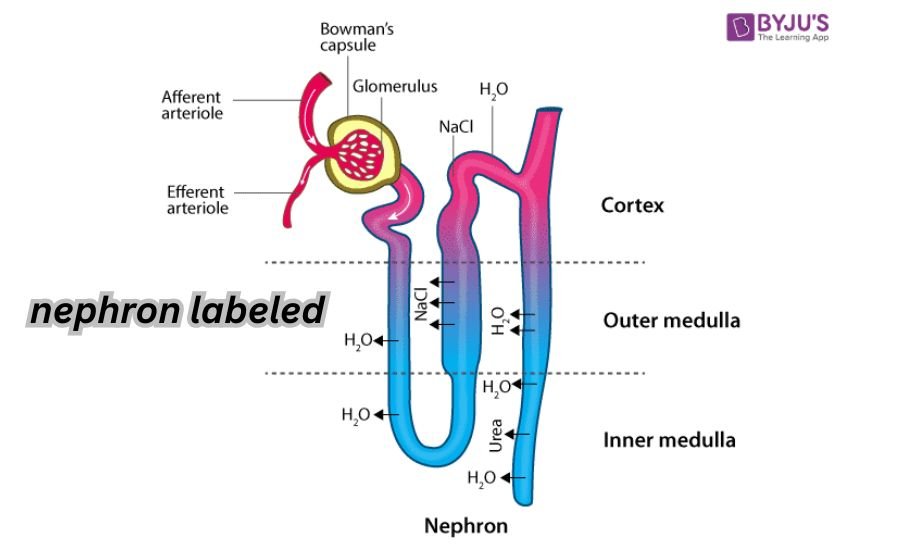
Loop of Henle: Concentration Specialist
The loop of Henle has two sections: the descending and ascending limbs.
- Descending Limb: Permeable to water, allowing reabsorption into the bloodstream.
- Ascending Limb: Impermeable to water, but reabsorbs salts.
This part of the nephron creates a concentration gradient, which is vital for water reabsorption in later stages.
Read More Blog : Discovering the Power of SemanticLast.com
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
The distal tubule fine-tunes the composition of urine by selectively reabsorbing ions and water. It’s influenced by hormones like aldosterone, which helps regulate blood pressure.
Collecting Duct: The Final Step
The collecting duct receives filtrate from multiple nephrons, concentrating urine before passing it to the ureters. Hormones like antidiuretic hormone (ADH) determine water reabsorption here.
How Nephron Labeled Enhances Understanding
Labeling the nephron not only clarifies its structure but also enhances comprehension of its function in health and disease. For example, identifying parts like the loop of Henle and its role in concentration gradients can explain conditions like dehydration or overhydration.
Common Disorders Related to Nephrons
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Damage to nephrons over time can lead to reduced kidney function, necessitating treatments like dialysis or transplantation.
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
A sudden loss of kidney function often results from trauma, infection, or medication side effects.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Damage to the glomeruli causes protein loss in urine, leading to swelling and other complications.
Understanding nephron labeling helps medical professionals diagnose and manage these conditions effectively.
Tips for Studying Nephron Labeled Diagrams
Visualize Each Part: Use colorful diagrams to highlight each labeled section.
Relate Function to Structure: Understand how each part contributes to the overall function.
Practice Regularly: Label blank diagrams to reinforce learning.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding how a nephron labeled unlocks critical insights into its structure and function. From the renal corpuscle to the collecting duct, each part plays a vital role in maintaining balance in the body. At blogrouters.com, we aim to provide clear and simple explanations to make learning engaging and effective. Whether you’re a student, a healthcare professional, or simply curious, exploring nephron anatomy can help you appreciate the incredible work your kidneys do every day.
Kidney health is crucial for overall well-being, and understanding the nephron is the first step toward better care.
FAQs
Q: What is the main function of the nephron?
A: The nephron filters blood, removes waste, and maintains fluid and electrolyte balance in the body.
Q: How many nephrons are in a kidney?
A: Each kidney contains approximately 1 million nephrons.
Q: Why is labeling a nephron important?
A: Labeling helps in understanding its structure and function, aiding in medical education and diagnosis.
Q: What role does the loop of Henle play?
A: The loop of Henle concentrates urine by reabsorbing water and salts.
Q: How can nephron damage affect health?
A: Damage to nephrons can lead to kidney diseases like CKD or nephrotic syndrome, impacting overall health.